Skins (156)
Visuals (115)
Input Plug-ins (34)
Output Plug-ins (6)
General Plug-ins (14)
Archive Reader (15)
Input Plug-ins (41)
DSP Plug-ins (10)
External Add-ons (16)
XMPlay Archive (71)
Skins (156)
Visuals (115)
Input Plug-ins (34)
Output Plug-ins (6)
General Plug-ins (14)
Archive Reader (15)
Input Plug-ins (41)
DSP Plug-ins (10)
External Add-ons (16)
XMPlay Archive (71)
The response speed to all these options is dependant on the buffer size, the delay will be the length of the buffer chosen in the Device section of the Options and stuff window.
Tip: These options only effect the playback of MOD file formats (MO3/XM/IT/etc) and can also be found under the MOD section of the Options and stuff window.
![]() Linear
Linear
![]() Sinc
Sinc
Linear 2 point interpolation "draws" a straight line between the samples, Sinc 8 point interpolation "draws" a smooth curve between the samples and requires more CPU power (Supports 3DNow! Technology.).
Linear interpolation gives decent sound quality with minimal cpu usage.
Sinc interpolation has, as a result of its complexity, far higher sound quality, with the price of higher cpu usage.
Interpolation can also be disabled. This is useful for older module to provide a crisper sound.
![]() Normal
Normal
![]() Sensitive
Sensitive
Ramping makes volume and panning changes smoother so that sudden large volume/panning changes do not cause any "clicking" in the sound.
It also fades-in (very quickly) new samples so that there is no click from them.
Sensitive ramping only performs the fade-in when it's neccessary to prevent a click, so percussive sounds stay sharp.
![]() "Normal" surround adds a phased surround sound feeling to modules.
"Normal" surround adds a phased surround sound feeling to modules.
![]() "Mode 2" ignores panning, so is good for mono MODs.
"Mode 2" ignores panning, so is good for mono MODs.
The higher the setting, the more sounds are pushed away from center. Obviously can only affect things when playing in stereo.
Tip: These options can also be found under the DSP section of the Options and stuff window.
![]() Normal
Normal
![]() Fade-In
Fade-In
![]() Dynamic
Dynamic
This is different to the volume slider. The volume slider controls the level of the sound card output, the amplification slider controls the level of the actual decoding.
The higher the amplification, the greater the dynamic range of the decoding output, but if it's too high clipping may occur resulting in distortion of the sound. Right-click options:
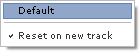
"Default" sets the amplification level back to its default amount (0.0 db).
"Reset on new track" resets the amp level when a track is loaded.
This causes the amplification level to be automatically reduced whenever clipping occurs. With fade-in enabled, it will fade-in new tracks until they clip, then it'll behave the same as normal. Dynamic mode continues to increase and decrease the amplification level throughout playback.

![]()
These are two built-in DSP settings that are available by default to improve the sound quality. The equalizer comes with some presets which may be selected by right-clicking the Equalizer button. The left reverb slider controls the frequency cutoff, i.e. the crispness of the reverb sound. The right slider controls the reverb level. Note that the reverb length is currently not adjustable.
When switched on, this enables the automatic loading of settings that have been saved for the track being loaded. Right-clicking brings up options to load settings specific to the file, load settings for the file's path, and load presets.
Tip: Advanced settings and further information can be found in the Saved settings section of the Options and stuff window.